- General Scenario and Current Trend :Total geographical area of the state is 93.60 lakh ha, having 56.03 lakh ha of Net Sown Area. Cultivable wasteland, current fallow and other fallow is 8.5% of the geographical area. Piedmont swamp soil, Terai soil and the Gangetic alluvium are three major types of soil available in the state. 1.53 lakh ha area has salinity and alkalinity, soil acidity is also a problem in parts of the state.
Annual average rainfall is 1205 mm. 45.67 lakh ha is irrigated area but varies across different regions ranging from a low of 16% to a high of 86%.
Very low level of Seed Replacement Ratio has been observed in the majority of the crops; however, increase in maize productivity is a success story.
As per 3rd Advance Estimates of 2008-09, productivity of rice in the state has been reported as 1584 kg/ha, wheat 1932 kg/ha, jowar 1035 kg/ha, bajra 1076 kg/ha, maize 2439 kg/ha, jute 1268 kg/ha, total pulses 846 kg/ha, total oilseeds 959 kg/ha, sugarcane 41157 kg/ha, Jute 1268 kg/ha.
An area of 2.91 lakh ha is under fruit plants having productivity of 10.9 MT/ha and 8.23 lakh ha is under vegetable cultivation and productivity is 17.1 MT/ha. 57% of banana, 53.3% of litchi, 17.5% of tomato, 17.5% of potato, 12.9% of guava, 11% of vegetables, 6.3% of mango and 5.2% of lemon of the country is grown in Bihar.
Agriculture and allied sector contributes approx 30% to the State GSDP.
-
Strength: Three agro climatic zones, wheat and rice occupies 81% of the gross cropped area, fertile soil, abundant ground water and water resource, easy availability of farm labour, suitable climate for whole range of vegetables, variety of roots and tuber crops, perennial fruit crops like mango, litchi, guava and lime, annual fruit crops like banana, pineapple and papaya, spices like ginger, turmeric and chilly, pulses and maize productivity fruit and vegetable production, honey production.
-
Limitation: Frequent floods, low SRR and VRR in all crops, lack of infrastructure for agriculture and allied departments including manpower, weak extension set-up, inadequate support from SAU/ research, non-availability of adequate quantity of quality seeds, planting material and seedlings, farm credit and insurance is much below the requirement.
- Public Investment : The state has made a few interventions to increase production and productivity through
Centrally Sponsored Schemes as well as through State Plan allocations in the recent years. In 2005-06,
agricultural sector received Rs.146.61 cr (3.28%), in 2006-07 Rs.273.06 cr (3.19%), in 2007-08 Rs.283.74 cr
(2.96%) and Rs.564.46 cr (4.31%) was the share of agriculture and allied sector in 2008-09 out of the State
Plan.
Government of India provided Rs.57.77 cr under RKVY, Rs.11.00 cr under ISOPOM, Rs.30.42 cr under MMA, Rs.2.69 cr under NHM, Rs.0.40 cr under Jute Mission, Rs.14.63 cr under ATMA, Rs.36.30 under NFSM during 2007-08.
During 2008-09, Rs.148.54 cr under RKVY, Rs.8.0 cr under ISOPOM, Rs.45.93 under MMA, Rs.31.22 cr under NHM, Rs.0.20 cr under Jute Mission, Rs.22.55 cr under ATMA, Rs.81.05 cr under NFSM was provided. Thus in last two years of the 11th Plan Period, State Government made an investment of about Rs.850 cr and GOI provided approx Rs.500 cr for agriculture and allied sector development. State intervention in the sector is low in comparison to the sector?s contribution to the GSDP.
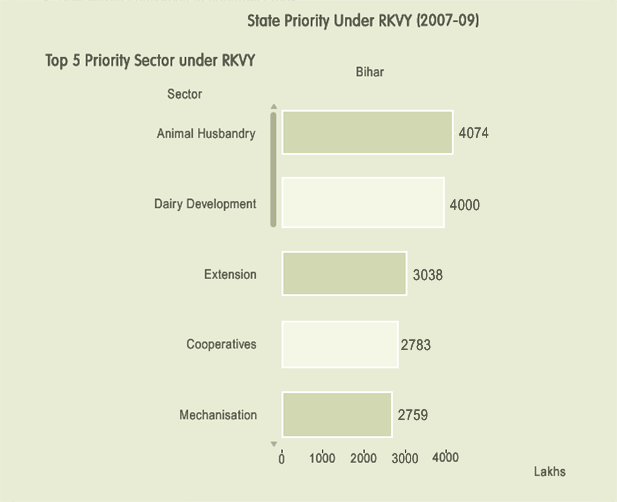
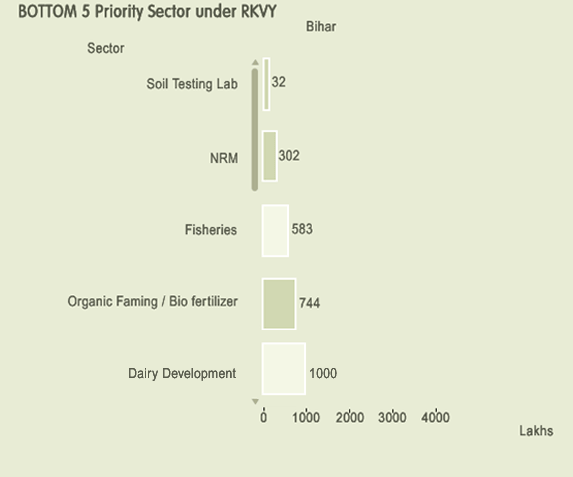

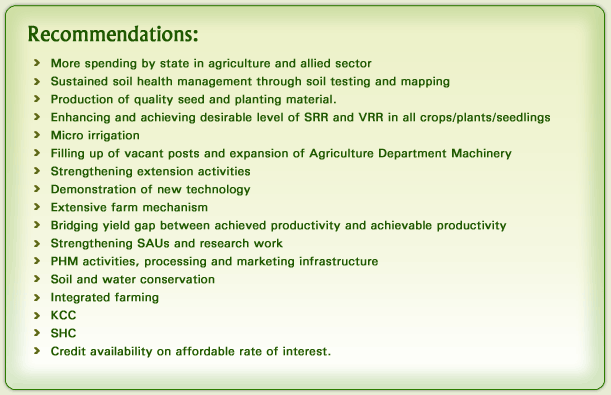
STATE HAS AGREED TO PREPARE TIME BOUND ACTION PLAN FOR THE STRATEGY AND RECOMMENDATION..